What Are Aml Typologies For Money Service Businesses
Background of AML CFT
Financial institutions are very vulnerable to the possibility of existence used as a media for money laundering (ML) and terrorism financing (TF), due to many transaction options for perpetrators of offense to commit an offence. Through various transaction options, such every bit transfer transactions, financial institutions become the entrance of assets that are the proceeds of crime or terrorism financing activities into the financial organization which tin be utilized for the benefit of perpetrators of law-breaking. For case, ML perpetrators tin can withdraw proceed of crime that appear legitimate and conceal the origins of illegally obtained. Whereas, TF perpetrators utilize keep of crime to finance terrorist activities.
Equally the development of products, business organisation model, engineering and information become increasingly complex, all Financial Service Providers nether the supervision of Bank Indonesia are required to implement the AML and CFT programs optimally and effectively. The AML and CFT program is not only of import for eradicating ML and preventing TF, all the same as well to back up the prudential principles which can protect the Service Providers and users from various risks that may ascend.
AML CFT to Achieve SPI Vision 2025
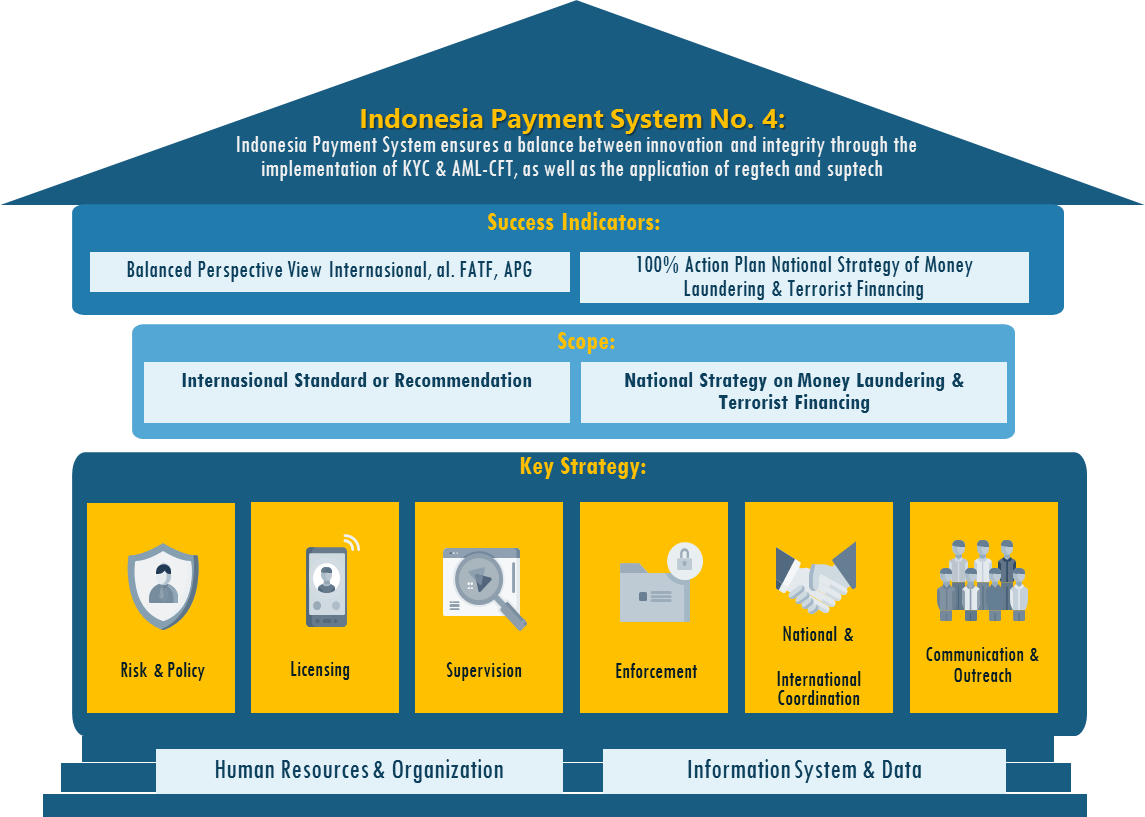
The Indonesian Payment Organization (SPI) 2025 guarantees a residuum between innovation and the integrity of the payment arrangement, through the application of Anti-Money Laundering, Counter Financing of Terrorism, and Prevention of Proliferation of Weapon of Mass Destruction Financing as Vision iv of the SPI 2025 Pattern "SPI 2025 guarantees a rest between innovation and consumers protection, integrity and stability equally well as fair business competition through the application of KYC & AML CFT, the obligation to disembalm data/information /public business, and the application of regtech and suptech as obligations in reporting, regulatory and supervisory".
The SPI 2025 Design publication can be downloaded here.
AML CFT Framework at Banking company Indonesia
The AML CFT Framework was congenital to support the SPI Vision 2025 and prevent coin laundering, terrorism financing, and funding for the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction that pose various risks, including:
- Threatening economic stability and financial system integrity;
- Reducing Indonesia's credibility in the international view;
- Increasing investment risk;
- The terrorism financing is one form of threat to the state's sovereignty.
The outcomes of the AML CFT Implementation on the SPI are as follows:
- The integrity of the Indonesian fiscal system that supports economic stability;
- The brownie and reputation of Indonesia increases internationally, with compliance with international standards;
- The integrity of the Indonesian financial organization supports the investment climate;
- Terrorism can be mitigated through the prevention of terrorism financing.
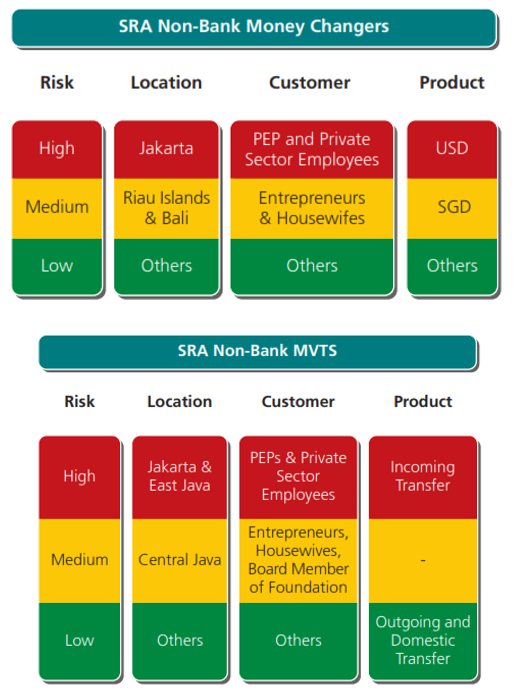
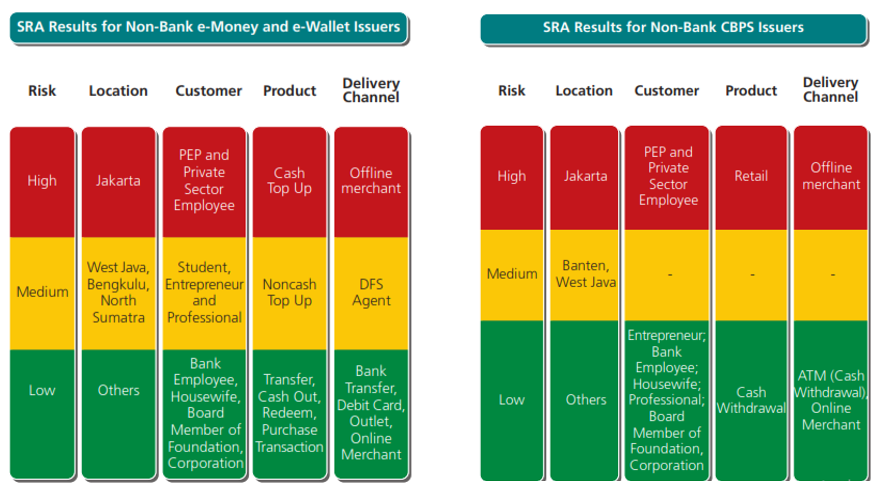
Sectoral Risk Cess (SRA)
Banking concern Republic of indonesia has been conducted the gamble assessment of ML and TF in the sector of non-bank payment system service provider and money changers. The cess is based on geographic, customer, products and services, and delivery channels. The risk assessment is outlined in the Sectoral Chance Cess (SRA) which refers to the National Risk Assessment (NRA). The purpose of the SRA adjustment as follows:
- to identify and analyze the potential and vulnerability of ML and TF; and
- to analyse the key risks of ML and TF, which involves mapping the risks interms of the geographic, customer, products and services, and delivery channels.
NRA on Terrorist Financing publication can be downloaded here
AML CFT Policy
As a Supervisory and Regulatory Bodies (LPP), Bank Indonesia has issued Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. xix/10/PBI/2017 concerning the Implementation of Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Terrorism Financing for Not-Bank Payment System Service Providers and Not-Bank Money Changers (PBI AML CFT).
The provisions contained in PBI AML CFT became effective in September 2017, targeting Non-Bank Payment System Service Providers as well equally Non-Banking concern Coin Changers. The PBI also stipulates the AML CFT requirements specific to payment system service providers and Coin Changers every bit follows:
- tasks and responsibilities of the directors and active supervision of the Board of Commissioners;
- policies and written procedures;
- risk-management processes;
- human resources direction; and
- internal control system.
In compiling the PBI AML CFT, BI adopts various provisions, including:
- FATF 40 Recommendations;
- Human action No. 8 of 2010 concerning the Prevention and Eradication of Coin Laundering (ML Act);
- Act No. 9 of 2013 on the Prevention and Eradication of Terrorism Financing (TF Human action).
Abreast issuing the PBI AML CFT, Bank Indonesia besides issues other BI Regulations that refer to the PBI AML CFT, including:
- PBI No.14/ii/PBI/2012 concerning Non-Bank Issuers of Card Based Payment Musical instrument;
- PBI No.xiv/23/PBI/2012 concerning Fund Transfer;
- PBI No.xviii/20/PBI/2016 concerning Non-Banking company Coin Changers;
- PBI No.18/40/PBI/2016 concerning the Implementation of Payment Transaction Processing;
- PBI No.19/12/PBI/2017 concerning the Implementation of Financial Engineering;
- PBI No. 20/6/PBI/2018 concerning Electronic Money.
Bank Republic of indonesia besides issued technical guidelines derived from the PBI AML CFT, including:
- Guidelines on the implementation of Hazard Based Approach of AML CFT (RBA);
- Guidelines on Know Your Customer (Customer Due Diligence) for Non-Bank Payment System Service Providers and Non-Bank Coin Changers.
- Guidelines on the implementation of firsthand blocking of fund endemic by individuals or corporations the identities of which are listed in the List of Suspected Terrorists and Terrorist Organizations (DTTOT);
- Guidelines on the implementation of immediate blocking of fund owned by individuals or corporations the identities of which are listed in the Listing of Funding of Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction;
Technical Guidelines AML CFT
Risk Based Approach (RBA)
In accordance with FATF Recommendation No. 1, Providers must identify and understand the risks of money laundering and terrorism financing covering geographic, customer, products and services, and delivery channels. As well as referring to the PBI AML CFT, Risk Based Arroyo (RBA) is used to improve the quality of supervision in society to forbid misuse of Non-Bank Payment Organisation Service Providers and Non-Bank Money Changers as media for money laundering and / or terrorism financing.
The application of a Risk Based Approach (RBA) includes:
- Offsite and onsite hazard-based supervision with risk ranking monitoring tools and RBA working papers;
- The Providers uses the RBA of AML CFT to behave risk and operational assessments.
Guidelines for the Implementation of Take chances Based Approach (RBA) for Non-Bank Money Transfer Services Providers and Non-Bank Coin Changers tin exist downloaded here
Guidelines for the Implementation of Gamble Based Approach (RBA) for Non-Depository financial institution East-Money and E-Wallet Issuers as well Non-Banking company Issuers of Carte du jour Based Payment Instrument can be downloaded hither
Guideline on Know Your Customer (Customer Due Diligence) for Non-Banking concern Payment System Services Providers and Non-Banking company Money Changers
In general, the procedures and mechanisms of Customer Due Diligence (CDD) implementation are regulated in accord with the PBI AML CFT. To facilitate greater understanding amongst Service Providers in terms of coming together and conducting CDD equally mandated past the PBI AML CFT, Depository financial institution Republic of indonesia published the CDD guidelines for Non-Bank Payment Arrangement Providers and Non-Banking concern Money Changers.
Some highlights in the CDD guidelines are equally follows:
- CDD guidelines are a reference that must be followed by Providers in implementing the CDD process for Service Providers, Service Users and benign owners, both conventional and electronic CDD (eastward-CDD).
- The application of e-CDD is the aforementioned as the application of conventional CDD, namely Uncomplicated CDD, Standard CDD, and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), by carrying out 4 (four) stages, namely identification, verification, on-going due diligence, and agreement the intentions and the purpose of the relationship.
- Providers implementing e-CDD, in principle, must comply with the rules regarding CDD implementation that take been stipulated in the PBI AML CFT, including applying due east-CDD to Beneficial Owners.
- In case Service Provider carries out ane of the e-CDD processes, the implementation of the process shall be carried out with due observance of the implementation of the east-CDD process which is stated in this Guideline.
Guidelines of Know Your Customer/Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Principles for Non-Bank Payment System Service Provider and Non-Bank Money Changer can exist downloaded here.
List of Suspected Terrorists and Terrorist Organizations (DTTOT)
Based on Act No. nine of 2013 concerning the Prevention and Eradication of Terrorism Financing, terrorism financing is divers as the direct or indirect use of funds for terrorist acts. The scope of terrorism financing includes direct and indirect actions to brand available, accumulate, provide or lend funds to terrorists or for terrorist acts, including the proceeds of criminal offense or legally obtained wealth.
Suspicious Fiscal Transactions on TF are:
- Financial transactions with the intent to be used and / or which are known to be used to commit terrorism; or
- Transactions involving Persons or Corporations whose name is listed in DTTOT.
Legal Provisions Relating to the DTTOT
- Act No. 9 of 2013 on the Prevention and Eradication of Terrorism Financing (TF Act);
- Joint Regulation of the Supreme Court, the Indonesian Minister of Foreign Affairs, the Master of Law, the Head of the National Agency for Counterterrorism (BNPT) and Head of the Financial Transaction Reporting and Analysis Centre (PPATK) on the Inclusion of Identity of Persons and Corporations in DTTOT and Immediate Blocking of the Funds of Persons or Corporations whose proper noun is Listed in DTTOT;
- Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 19/ten/PBI/2017 concerning the Implementation of Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Terrorism Financing for Non-Banking company Payment System Service Providers and Non-Banking concern Coin Changers (PBI AML CFT).
In accordance with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Recommendation No. 6, Banking company Republic of indonesia forwarding the Indonesian National Police letter related to DTTOT information and blocking orders to all Not-Bank Payment Organisation Service Providers and Not-Bank Money Changers, followed upward with the obligation to immediately blocking all funds owned or controlled, by any person or corporation listed in the DTTOT. Guidelines on the implementation of immediate blocking of fund owned by individuals or corporations the identities of which are listed in the list of suspected terrorists and terrorist organizations can exist downloaded here
The complete list of Suspected Terrorists and Terrorist Organizations (DTTOT) and the Immediate Blocking of Funds endemic by Persons or Corporations Listed in DTTOT can exist downloaded here
DTTOT Flow of Data
UNSC; Ministry of Foreign Affairs; National Police force; Central Jakarta District Court; Depository financial institution Indonesia; Payment System Service Providers/Money Changers
DTTOT Catamenia of Information ; Flow of Information from Service Providers
Listing of Financing the Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Devastation (WMD)
Based on the Articulation Regulation of the Minister of Strange Affairs of the Democracy of Indonesia, Principal of the National Police of the Republic of Indonesia, Chairperson of the Indonesian Fiscal Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre (INTRAC) and Chairperson of the Nuclear Energy Supervisory Agency, WMD proliferation is defined equally the proliferation of nuclear, biological and chemical weapons using the gain of criminal offence or wealth obtained legally.
Legal Provisions Relating to the Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction
- Articulation Regulation of the Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Indonesia, Caput of the Indonesian National Constabulary, Head of the Center for Reporting and Analysis of Financial Transactions, and Head of the Nuclear Free energy Supervisory Bureau on Inclusion of Identity of Persons and Corporations in the Listing of Funds for the Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Devastation and Blocking and Accidental Buying of Owned Funds or Corporations that are listed on the list of funding for the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
- Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 19/10/PBI/2017 concerning the Implementation of Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Terrorism Financing for Not-Bank Payment Organization Service Providers and Non-Banking concern Coin Changers (PBI AML CFT).
In accordance with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Recommendation No. 7, Banking concern Indonesia transmits data on the proliferation of weapons of mass devastation from PPATK to the providers and is followed up with the obligation to immediately block all funds endemic or controlled, directly or indirectly, by persons or Corporations based on the Register of Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction. Guidelines on the implementation of immediate blocking of fund owned by individuals or corporations the identities of which are listed in the list of funding of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction can be downloaded hither
The complete List of Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction Financing can be downloaded here
Period of Data concerning Financing the Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction
UNSC; Ministry of Foreign Affairs; Indonesian Financial Transaction Reports and Assay Centre (INTRAC); Depository financial institution Indonesia; Payment System Service Providers/Money Changers
WMD Proliferation Flow of Information ; Flow of Information from Service Providers
Information concerning the List of Suspected Terrorists and Terrorist Organisations (DTTOT) and List of Financing the Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) is available for download.
National and International Cooperation related to AML CFT
BI continues to aggrandize the AML CFT cooperation with relevant government, both national and international in lodge to strengthen the implementation of AML CFT.
- National Cooperation
Bank Indonesia continues to actively and continuously coordinate with the Financial Transaction Reports and Assay Center (PPATK), the Corruption Eradication Committee (KPK), the Financial Services Authorization (OJK), the Indonesian National Police force (POLRI), the National Narcotics Bureau (BNN) and other relevant agencies to strengthen the implementation of AML CFT.
- International Cooperation
Bank Indonesia is actively cooperating with Bank Negara Malaysia, Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, Banking company of Thailand. BI continues to make efforts to expand AML/CFT cooperation with other foreign authorities.
a. Membership in the APG
APG Contour
Asia / Pacific Group on Money Laundering is a regional organization (Asia Pacific) to prevent and eradicate coin laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation funding activities. Indonesia has been a member of APG since 2001.
Mutual Evaluation
Every country that is a member of APG is committed to implementing Common Evaluation (ME) to appraise the level of compliance with FATF Recommendations as an international standard of Anti-Money Laundering and Counter Financing of Terrorism (AML CFT).
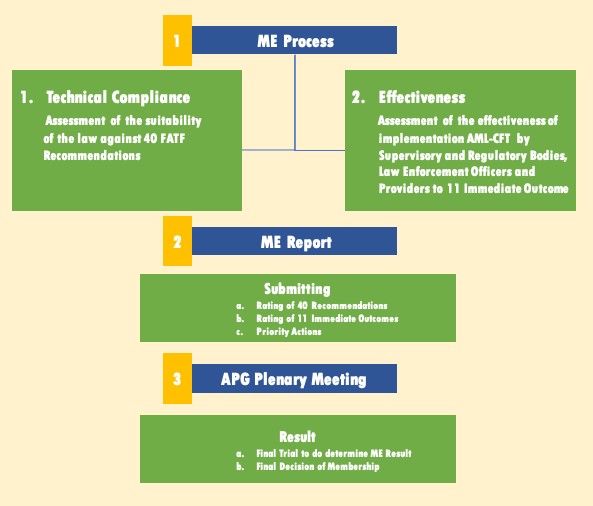
APG Mutual Evaluation Result
The 21st Asia / Pacific Grouping (APG) on Coin Laundering session held on July 21-27 2018 in Kathmandu, Nepal, has ratified the Indonesian Mutual Evaluation Report (MER). The MER is the outcome of a review of Republic of indonesia's compliance and effectiveness of anti-money laundering and terrorism financing regimes that are based on xl Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations.
Assessment of compliance with efforts to prevent and eradicate criminal acts of coin laundering and financing of terrorism is carried out in a professional person and objective manner. The MER Indonesia assessor team has representatives from the United States, Canada, Macao-Prc, China-Taipei, Pakistan and Bangladesh and the APG Secretariat.
The APG Annual Session in Kathmandu, Nepal has determined that compliance and effectiveness of Republic of indonesia'due south implementation of international standards in the field of prevention and eradication of criminal acts of money laundering and financing of terrorism, is considered to exist very adequate. Of the forty FATF recommendations related to legal framework compliance, Indonesia received a 'C' (compliant) rating or the highest score for 6 recommendations. And then got an 'LC' (Largely Compliant) rating for 29 recommendations, and got a 'PC' (Partially Compliant) rating for four recommendations. Of the overall recommendations there is merely i recommendation in which Republic of indonesia received a 'NC' (Non-Compliant) rating, namely on recommendations related to funding for the proliferation of weapons of mass devastation.
Regarding the effectiveness of implementation, Indonesia received a Substantial rating for 5 Immediate Outcomes (IO), and then a Moderate rating for 5 IO, too every bit a Depression rating for 1 IO related to funding for the proliferation of weapons of mass devastation. The results of the assessment indicate that the effectiveness of the implementation of APU / PPT in Indonesia is better when compared to APG countries such as Australia, Malaysia and Singapore.
The complete written report of Indonesia's APG Common Evaluation Report (MER) can be downloaded here
b. Preparation towards FATF Total Membership
The Fiscal Action Task Force on Coin Laundering (FATF) is an inter-governmental arrangement formed in 1989 by the G-7 with the aim of developing systems and infrastructure to prevent and combat money laundering, terrorism financing, and funding for the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
FATF sets standards, namely FATF forty Recommendations and procedures (policy making) and encourages the effectiveness of its implementation through legal instruments, regulations and other media (recommendations) to combat coin laundering, terrorist financing and weapons of mass devastation that volition threaten the integrity of the financial system. In its operations, FATF monitors the implementation of recommendations issued to its members, reviews technical and eradication media and encourages the implementation of its recommendations globally
Benefits of Beingness a Full Member
- Acceleration to become a country recognized as having loftier financial system integrity by applying international standards to prevent crime in the financial sector.
- Be a potent basis going forrad for the development of Indonesia'south economy in the world, where this can better Indonesia'south ranking in various aspects, including investment.
- A means to demonstrate Indonesia's leadership equally a major country, especially in Asia and emerging markets, which of course can take a positive bear upon on the development of the domestic economy.
- Can play an active and foremost role in setting AML CFT international standards that are beneficial for the development of the domestic AML CFT framework and the grooming of futurity policy responses for emerging markets.
- The effectiveness of the formulation of stance between Indonesia and Banking concern Indonesia, especially in discussions in international forums.
Roadmap towards FATF Membership for Indonesia
BI'southward Strategy in supporting Indonesia to go a FATF Full Fellow member
In supporting the Government'southward efforts to get a Full Member of FATF, Banking company Indonesia has prepared 3 strategies, namely
- Fulfillment of all FATF recommendations for the payment arrangement sector and foreign exchange business activities in preventing and eradicating coin laundering, terrorism financing, besides as the proliferation of weapons of mass devastation financing.
The effective awarding of AML-CFT principles is believed to exist able to support the integrity of the financial system in Indonesia, increase Indonesia'due south credibility and reputation, and comply with applicative international AML-CFT standards. In the context of setting the AML-CFT principles, BI has issued provisions and guidelines regarding the implementation of the AML-CFT program for Not-Bank Payment System Service Providers (PJSP) and Non-Bank Coin Changers (KUPVA BB) and Financial Technology provisions. In the context of risk assessment, Bank Indonesia also prepared a Sectoral Hazard Assessment (SRA) and Risk Based Approach (RBA) Guidelines for PJSP SB & KUPVA BB and contributed to the training of a National Risk Assessment (NRA), Regional Hazard Assessment (RRA) on Corruption and SRA Virtual. Joint avails of related Ministries / Agencies that are coordinated past PPATK. In the context of payment system supervision, a chance-based approach is practical both by Providers and by BI itself. This is also stated in the new PBI AML-CFT which requires the Providers to apply a risk-based approach (RBA) in the implementation of AML-CFT. Meanwhile in terms of Supervision, the risk-based approach is applied both by the providers and by Bank Republic of indonesia itself. This is likewise outlined in the new AML-CFT Regulation which requires Providers to implement a risk-based arroyo (RBA) in implementing AML-CFT. - Increasing public awareness and institutional cooperation in preventing and eradicating money laundering, terrorism financing, and funding for the proliferation of weapons of mass devastation.
In terms of increasing public awareness, Bank Indonesia has educated the public to use licensed PJSP and KUPVA BB. In the context of institutional cooperation, Bank Indonesia collaborates with ministries and institutions in Republic of indonesia, including with the police to curb unlicensed Non-Banking concern Coin Changers (KUPVA BB) and illegal Not-Bank Fund Transfers (PTD BB) in Indonesian territory. Command against unlicensed Providers and the application of the Quick Response (QR) Code on the KUPVA BB and PTD BB logos are forms of protection for the public from money laundering and terrorism financing activities. In order to improve the implementation of the AML and CFT programs, Bank Indonesia has also strengthened cooperation and coordination intensively with relevant authorities such every bit the PPATK, BNN, and KPK to ensure the effectiveness of its implementation. In the context of international cooperation, Bank Indonesia is actively cooperating with Bank Negara Malaysia, Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, Banking company of Thailand, and other international institutions. - Improved coordination with Ministries and Institutions in the TPPU Committee in the technical grooming of the FATF Mutual Evaluation for Indonesia, particularly in sectors under the dominance of Bank Indonesia.
Proposition of Strengthening AML CFT in Responds of Covid-19 Pandemic
In May 2020, FATF had published the proposition related to challenges, skillful practices and policies in responding of Coin Laundering and Terrorist Financing threats and vulnerabilities namely COVID-19 related Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing - Risk and Policy Responses.
The suggestion including:
- Coordinate domestically and effective communication need to be washed between Regime and Providers related to the effect of COVID-19 pandemic in AML CFT Program.
- Urge Providers to utilize Adventure Based Approach in doing their Know Your Client or Client Due Diligence.
- Urge Providers to apply electronic and digital payment.
Depository financial institution Indonesia besides suggests its Providers (Not-Banking company Payment System Service Providers and Coin Changers) to stay vigilant during Covid-19 pandemic.
Bank Indonesia suggestion including:
- Awareness
Understand the gamble of Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing related to the consequence of COVID-nineteen in their businesses. - Arrange
Assess the impact of COVID-nineteen to Provider'southward AML CFT policy co-ordinate to FATF recommendation, e.g. expansion the implementation of electronic and digital payment and the implementation of electronic Know Your Customer (e-KYC) or Customer Due Diligence (CDD). - Action
Encourage in using risk based arroyo and coordinate with related Institutions too Supervisor in Bank Republic of indonesia.
Suggestion from FATF which is COVID-xix related Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing - Gamble and Policy Responses tin can be downloaded here
Relevant Printing Releases and Latest Info
Entrada Cloth

#CombatingMoneyLaundering
# CombatingTerrorismFinancing
Let'due south Transact Safely and Securely
Us e Licensed Money Changers and Funds Transfer Service Providers
Present National Identification Card to initiate transaction or payment
Report Unlicensed Money Changers and Funds Transfer Service Providers to Bank Indonesia
Violators are Subject field to Imprisonment and Fines
(Act No. 8 of 2010 and Human action No. nine of 2013)
Source: https://www.bi.go.id/en/fungsi-utama/sistem-pembayaran/anti-pencucian-uang-dan-pencegahan-pendanaan-terrorisme/default.aspx
Posted by: judemisaid.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are Aml Typologies For Money Service Businesses"
Post a Comment